The State of Vulnerability Management
In today’s ever-evolving digital landscape, safeguarding sensitive information and critical systems against cyber threats is more challenging than ever. The volume and complexity of vulnerabilities continue to rise due to factors like rapid technological innovation, open source library adoption, an expanding attack surface that now includes the cloud, the proliferation of software applications, and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats.
Many organizations face resource constraints, including limited budgets, personnel shortages, and competing priorities, making it difficult to keep pace with the constant stream of vulnerabilities and effectively allocate resources to mitigate them. Patch management, while essential, presents its own challenges. Timely patching without disrupting critical systems and operations requires careful coordination and testing, straining organizational resources and introducing potential risks.
A one research study from 2023, organizations take an average of 88 days to patch critical vulnerabilities and 208 days for low-severity vulnerabilities, providing attackers ample time to gain access to corporate networks. In many cases, vulnerabilities remain unaddressed even a year after discovery, exposing organizations to unsophisticated attacks.
According to IBM’s 2023 Cost of a Data breach Report, 67% of breaches were discovered by third parties rather than internal resources, highlighting the need for organizations to gain better control over vulnerability management.
The Risk Based Vulnerability Management
When taking a risk-based approach to threat and vulnerability management, you prioritize vulnerabilities based on the level of risk they pose and their potential impact on your organization’s assets, operations, and objectives.
It is important to keep in mind the difference between risk vs vulnerability. A vulnerability is simply a weakness or a flaw in a system, network, application, or process. When exploited by a malicious actor, it can compromise sensitive data or systems. The risk refers to the likelihood that the threat will be exploited and the potential impact that a breach may have on your organization.
Risk-based vulnerability assessment does not rely only on industry standards (like, for example, a CVSS score) to determine which vulnerabilities are the biggest threat. Instead, it also takes into account how the vulnerability affects your organization. In other words, the risk. For example, if a vulnerability with a “severe” rating only affects an isolated asset that doesn’t deal with any sensitive information, it may not be a priority for you under risk-based vulnerability management.
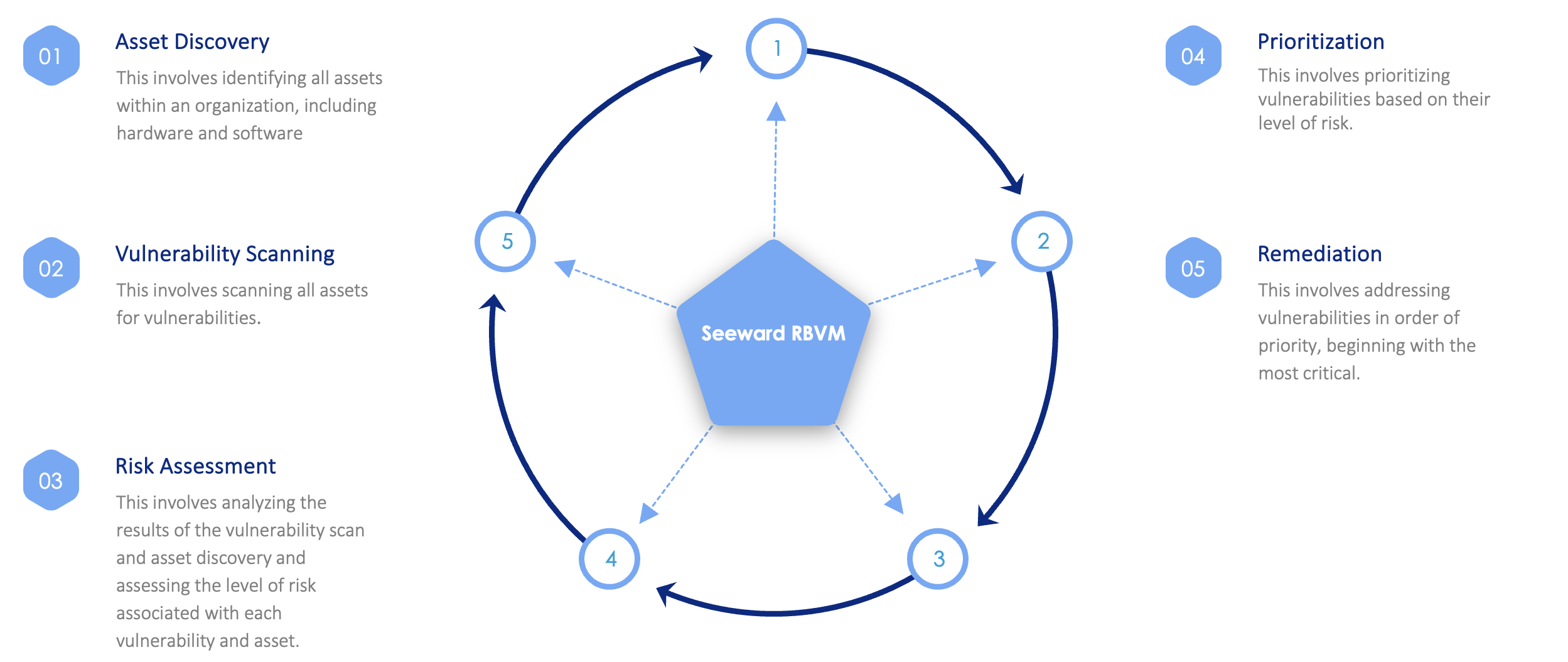
Implementing a Risk Based Approach
Given these challenges, the need for a risk-based approach to vulnerability management has never been more apparent. A risk-based approach involves prioritizing vulnerabilities based on their potential impact on the organization’s assets, operations, and strategic objectives. By focusing on the most critical vulnerabilities first, organizations can optimize their limited resources and enhance their overall security posture.
Conclusion
The transition to a risk-based approach is essential to address the growing complexity and dynamic nature of cyber threats and vulnerabilities. By prioritizing vulnerabilities based on risk and aligning security efforts with business objectives, organizations can enhance their resilience to cyberattacks, optimize resource allocation, and maintain a proactive security posture in today’s increasingly digital world.
